Case

Case
After the steam is generated by the boiler, it is contained in a pressure pipe and transported to the heat exchange equipment.
We call this transported steam pipe network a heat network.
When the steam pipeline starts, the normal temperature steel pipeline, pipeline accessories, flanges, etc. must be heated to close to the steam temperature, which will cause part of the steam to condense.
When the steam flows in the heat network, good insulation measures must be taken, but it is still unavoidable that heat is dissipated to the environment due to the temperature difference between the external environment and the steam, resulting in the condensation of part of the steam. We call the two parts of the condensed steam as pipe loss.
The steam containing part of the condensed water will become moist and aggressive, and as the condensed water increases, the high-speed flowing steam will provide it with enough "water head" to form a "water bomb" with high kinetic energy.


We use steam, mainly using the latent heat of vaporization of steam. Water absorbs heat in the boiler and turns into steam. When the steam releases its evaporation enthalpy (latent heat)), the steam will condense into condensed water. It can be seen that steam, as the carrier of heat, can only generate benefits by releasing heat where heat is needed, and heat release anywhere else is waste.
Insulation can reduce the heat dissipation of steam pipes and valves and save energy. Any steam pipes, valves, flanges, joints, and containers need insulation.
The steam pipeline is insulated to reduce the steam condensation caused by heat dissipation, and avoid the erosion, vibration and water hammer caused by the condensed water moving with the steam at high speed on the steam pipeline, valve and heat exchanger.
If the steam pipe is not insulated, the steam flow rate must be reduced to transport the same quality of steam, requiring a larger steam pipe. If electronic components (actuators, positioners, solenoid valves, etc.) are installed on the valve, thermal insulation is conducive to the stable operation of the electronic components. If the sub-cylinders, valves and pipes in the boiler room are not insulated, the ambient temperature of the boiler room will even exceed 60°C.
Steam valves that often require manual contact or operation must be kept warm to avoid burns. Or to avoid the operator worrying about the valve closing problem caused by scalding.
On the one hand, the thermal insulation of the steam pipeline uses a thermal insulation material with a very low heat transfer coefficient as a barrier, and on the other hand, an air bag is formed inside the thermal insulation material, so as to take advantage of the low thermal conductivity of the air for thermal insulation. The insulation of pipeline equipment is relatively easy, and the construction can be done in accordance with the relevant specifications.
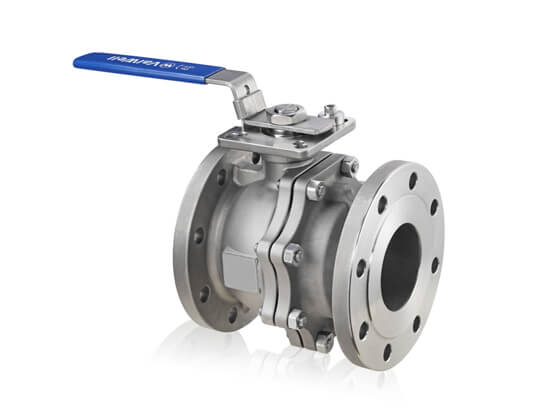



However, for steam pressure reducing valves, bellows seal globe valves, steam regulating valves, steam traps and other sizes of steam valves, their shapes are relatively complex, and the convenience of valve operation and maintenance should be considered, and it is often difficult to keep warm or difficult to maintain after heat preservation.
Commonly used valves in steam system include globe valve, ball valve, gate valve, check valve, safety valve, pressure reducing valve, steam trap, etc. The material should be carbon steel or stainless steel. If you have any questions for valves in steam system, you can freely contact WESDOM to get professional solutions.